The Covid-19 crisis in India has posed severe challenges to small and growing businesses in the country, widening the pre-existing gender gaps and diminishing considerable developments achieved within the women entrepreneurship ecosystem in the past decades.
In a bid to shed light on the unique and disproportionate impact of the pandemic on women-led businesses, GIZ has recently come out with a detailed report. The report titled “Women Entrepreneurs’ Resilience in Times of Covid-19” was based on GIZ’s Project Her&Now. The Her&Now project is implemented by GIZ (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit) on behalf of the German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) and the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Government of India.
The findings of the report will be based on a study conducted in December 2020. The data will be collated based on interviews of 211 women entrepreneurs operating across a diverse field of sectors.
Speaking about the report, Project Head Ullas Marar says says, “Given that the pandemic is far from being over and there are high possibilities we may have to tackle a third wave and subsequent waves in the near future, it has become imperative to understand the ways in which women-led enterprises (as well as the women entrepreneurs themselves) responded to the pandemic when it began, because we believe a lot of lessons and learnings lie there."
"Keeping that in mind, we have prepared, and are now glad to release the report -- “Women Entrepreneurs’ Resilience in Times of Covid-19” – which we believe will be of great help for the key stakeholders in deriving best practices, learnings and opportunities for the wider ecosystem of women entrepreneurship in India", he added.
The report comprises three main sections:
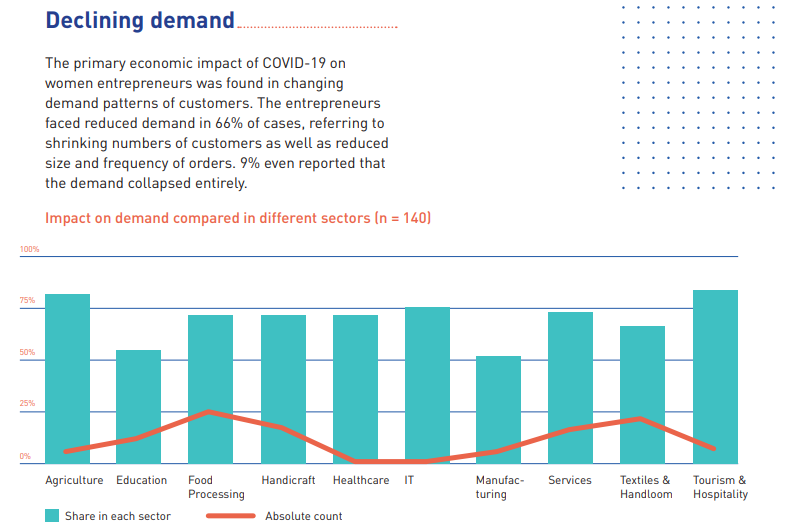
Impact of Covid-19 on women entrepreneurs: This section reveals that for most of the women entrepreneurs, their customer demand was being most affected in the aftermath of the pandemic, followed by issues relating to working capital and operational processes. Several entrepreneurs also struggled with accessing the marketplace, retaining employees and receiving supplies in time. A smaller share of the respondents experienced negative impacts relating to inventory.
Responsive measures by women entrepreneurs: This section highlights the key measures that women entrepreneurs took to counter operational disruptions, such as: efforts to market digitally, diversifying distribution channels, adjusting the product/service offering, re-adapting operations or revising the financial model, investing in business development, optimizing the supply chain, revising the pricing strategies, among others. By using either a few or most of these measures, many among the interviewed entrepreneurs were able to turn the Covid-19 induced challenges within their business environment into opportunities, reveals the report.
Conclusion: This section contains six important conclusions that can be drawn from the findings of the report and attempts to outline the optimal way forward for the women’s entrepreneurship ecosystem in India.
- 15811 reads









Add new comment